Apatite: Introduction, Properties and Uses
 Xingaonai
Xingaonai
![[list:date style=M.d,Y]](/images/date.png) Mar.18,2025
Mar.18,2025
 326
326
If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Introduction to apatite
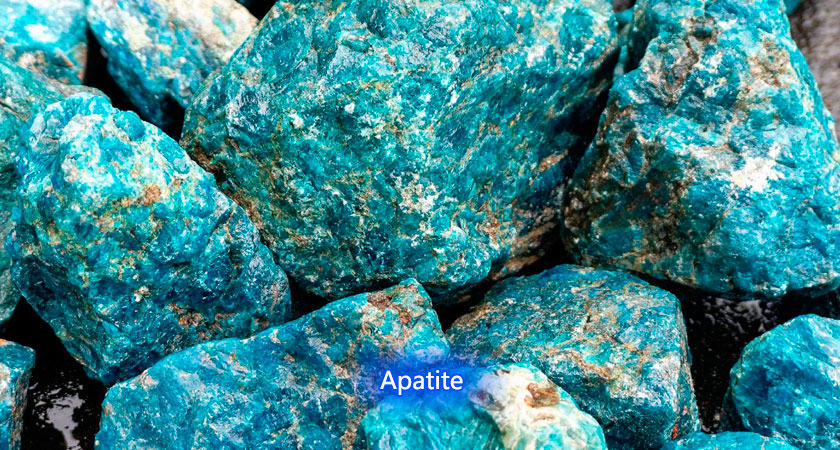
Apatite is a common phosphate mineral, the main component of which is calcium phosphate, and it has rich diversity. Apatite is generally grayish white or light yellow with a glassy luster. It not only contains many types of apatite, such as fluoroapatite, yellow-green apatite, etc., but also shows a variety of characteristics in shape and color. These glassy crystals, blocks or nodules of apatite often have hexagonal columns with conical tips, becoming a unique landscape in nature. Although most apatites are pure and transparent, if they are hard enough, they can be transformed into precious gemstones.

Formation of apatite
Apatite is an important mineral in the formation of igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Its formation is closely related to the deposition and metamorphism of phosphates. Apatite formed in igneous rocks is called endogenous apatite, which is usually enriched as a byproduct of basic or alkaline rocks; while apatite formed in sedimentary rocks is exogenous apatite, which is mainly produced by biological sedimentation or biochemical sedimentation processes and often appears in the form of nodules; in addition, apatite may also form in specific geological environments such as marine sedimentation, lake sedimentation and groundwater action.
Characteristics of apatite
Physical properties: Apatite is a mineral with a variety of colors, medium hardness and unique crystal structure. It is usually colorless, white, green, blue, purple, etc., with a glassy luster, transparent or translucent, and is a softer mineral with a hardness of 5.
Chemical properties: The chemical formula of apatite is Ca₅(PO₄)₃(F,Cl,OH), which is mainly composed of calcium and phosphate. Apatite can be divided into fluoroapatite, chlorapatite and hydroxyapatite according to its composition. In addition, apatite is stable at room temperature and pressure, difficult to dissolve in water, and may decompose in high temperature or strong acid environment.

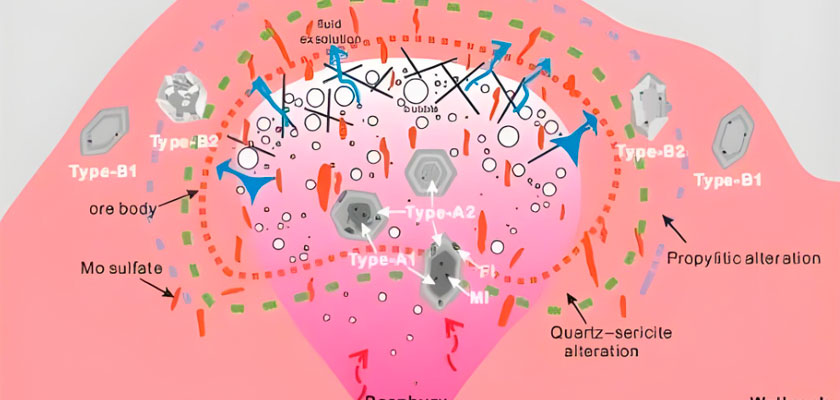
Apatite crystal structure
Apatite belongs to the hexagonal crystal system and is mainly composed of phosphate tetrahedrons and calcium ions. Usually, apatite crystal forms include columnar crystals, needle crystals, plate crystals, granular or block aggregates, fibrous aggregates, etc. The trace elements or crystal defects of apatite directly affect the crystal color, and common colors include colorless, white, green, blue, purple, etc.
Uses of apatite
Agriculture: Apatite is the main raw material for making phosphate fertilizers, which are essential for crop growth and can promote root development, flowering and fruiting, and disease resistance.
Chemical raw materials: used in the production of phosphoric acid, phosphorus compounds and other chemical products.
Metallurgical industry: used as a flux for metal smelting.
Ceramic glass: used to make special ceramics and glass to improve the chemical stability and mechanical strength of products.
Biomaterials: Hydroxyapatite is the main inorganic component of human bones and teeth and has good biocompatibility. Used to make artificial bones, tooth repair materials and biological coatings.
Environmental protection: Apatite can be used to remove heavy metal ions in wastewater because it has a strong adsorption capacity for heavy metals. It can also be used to fix heavy metal pollutants in the soil to reduce its harm to the environment.
Scientific research: Used to study geological processes, mineral deposit genesis and paleoenvironmental reconstruction.
Jewelry collection: Apatite has bright colors and high transparency, but low hardness, suitable for collection or making low-wear jewelry.
Food industry: As a food additive, it is used to supplement calcium and phosphorus.
Feed industry: As a phosphorus source for animal feed, it promotes animal growth.
Energy materials: Research on the application of apatite in solid electrolytes and fuel cells.

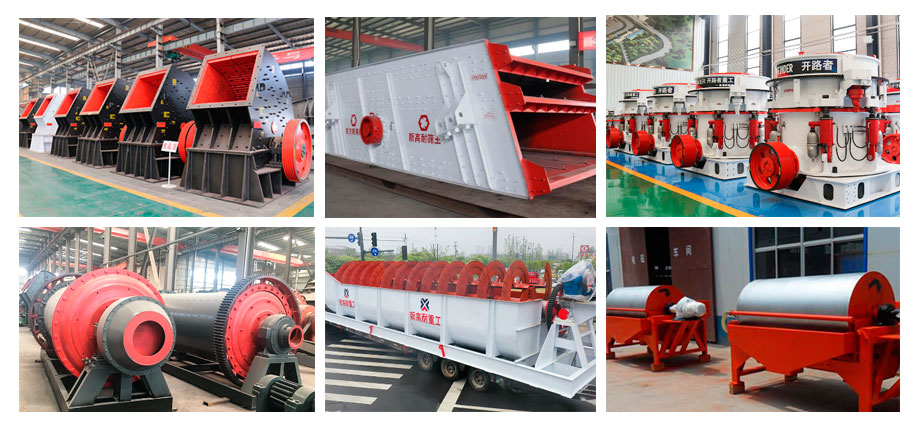
Apatite flotation process
Since apatite is used to extract phosphorus, the phosphate ore must be ground into fine powder. In the process of turning the ore into fine powder, it needs to be processed by a crusher and a ball mill. After the phosphate ore is turned into fine powder, it also needs to be sorted by a flotation machine. The flotation process is: crushing and screening, grinding, flotation, dehydration, and tailings treatment.
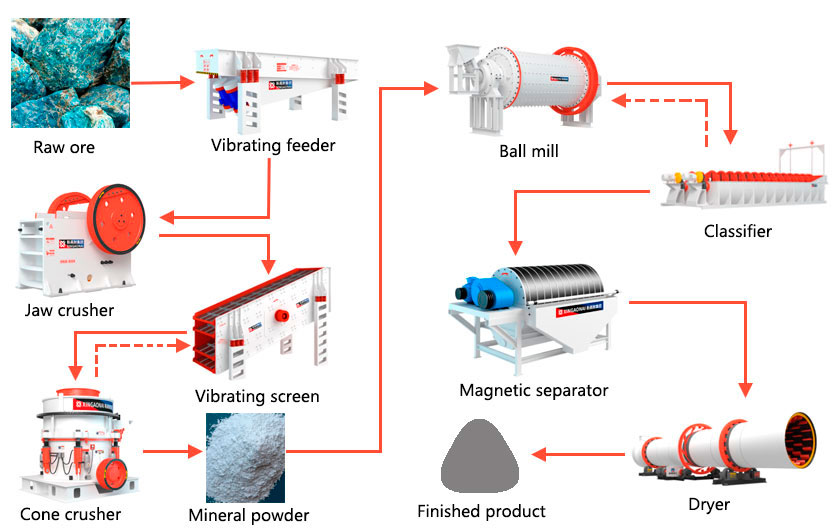
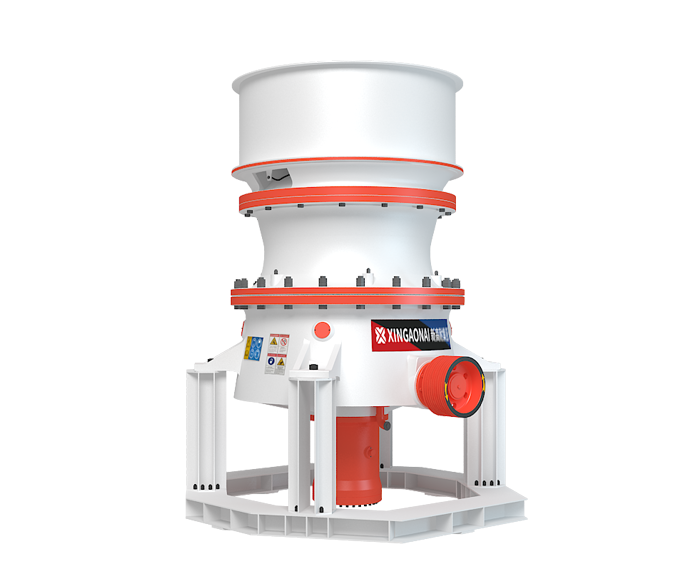
The main equipment includes vibrating feeder, jaw crusher, Cone Crusher, vibrating screen, pendulum feeder, ball mill, classifier, magnetic separator, concentrator, dryer, etc.

Author: Xingaonai
Reprint address: http://xingaonai.cn/products-knowledge/apatite-introduction-characteristics-uses.html
 +86 15637191339
+86 15637191339 sale@xingaonai.cn
sale@xingaonai.cn




 Message
Message Chat Now
Chat Now